Frequencies 5G: Arcep confirms the release of three new GHz bands, 5G – Radio waves
5G
A American study of the scientific journal Nature on 5G has highlighted the effects that might have the 5G frequencies on weather predictions in the United States. The frequencies envisaged for the development of 5G on the other side of the Atlantic will be located at first between 24.25 and 25.25 GHz.
5G frequencies: Arcep confirms the release of three new GHz bands

5G tests continue among operators. One of the priorities of the moment for the proper functioning of this new network is the award of suitable frequency bands. In its press release of June 11, 2019, the telecoms regulator announces the release of new frequencies. These will not be used before 2020. We take stock.
Network 5G: What are the new GHz frequencies allocated and why were they chosen by Arcep ?

In the world of telecommunications and beyond, everyone is preparing for the technological revolution that should bring 5g, The network that specialists call “The breaking generation“”. In 2018, ARCEP created a “5G” pilots “ devoted to the authorizations necessary for theuse of frequencies.
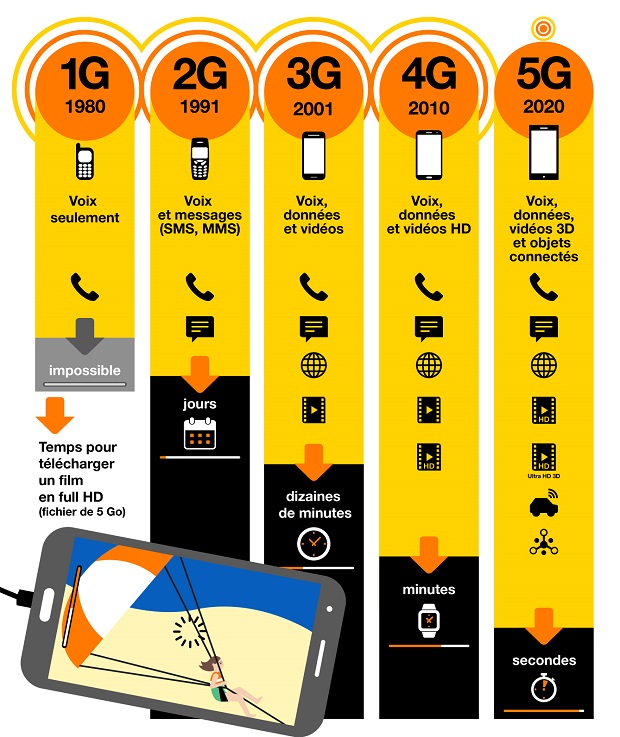
Arcep, in collaboration with theNational Frequency Agency (ANFR) therefore began to think about high frequency bands, conducive to ultra high speed of 5G. These new attributions also aim not to saturate the current, lower frequencies, used for 2G, 3G and 4G networks. THE millimeter waves of 5G will thus be able to evolve freely at a speed (for its beginnings) revolving around 1gbit/s (1000 Mbit/s). As an indication, the connection speed in 4G, 4G + and 4G++ is between 10 Mbit/s and 300 Mbit/s.
What are the frequency bands currently used in France for mobile networks 2G network (only calls and SMS) works on frequencies 900 and 1800 MHz, 3G network 1900-2100 MHz and the 4G network on 700, 800 and 1800 MHz as well as 1900-2100 MHz (for Bouygues Telecon and SFR since 2017). The frequencies of an electromagnetic wave are essential for the operation of a telecommunications network, without them and without waves, no possible coverage. To find out more, we advise you to consult our explanatory guide on electromagnetic frequencies.
Here are the three frequency bands envisaged for 5G:
- There 3.5 GHz band (3410 MHz-3800 MHz): Until 2026, it is used for various functions (such as the Radio THD) and should be one of the first open bands for 5G.
- There 26 GHz band (2650 MHz-2750 MHz): For the moment, only the 26.5-27.5 GHz band is free and can be used from 2020 for 5G.
- There 1.5 GHz band Or LAN (1427 – 1517 MHz): this is the third frequency band planned. This band is not available for the moment, it is used for interior and defense ministries for the collection of mobile networks. Depending on the authorizations of the arcep, this band could be free by the end of 2022. 1.5 GHz is not as high as the previous two and thus has advantages for the 5G coverage especially within buildings.
The operators and actors, mainly Orange, SFR, Bouygues Telecom and Free, wishing to use these frequencies for 5G, will have to Buy at auction scheduled for fall 2019. The latter could reach the three billion euros in France according to the President of Arcep, Sébastien Soriano, but not more. The idea is not to reach a staggering cost like in Germany for example, where they ended at 6.55 billion euros.
5G frequencies: where are the experiments in French cities ?
Arcep regularly keeps a list to list the cities and actors involved in tests on 5G. In general, one to three participants are there: often one of the four historic operators and/or a network manufacturer like Nokia or Ericsson.
11 Laboratories among 9 different municipalities have completed their experiments, it was: Paris (75), Lyon (69), Toulouse (31), Sophia Antipolis (06), Nozay (91), Cesson-Sévigné (35), Lanion (22), Mérignac (33), Saint-Ouen (93). And, to date, it still remains 36 5G active laboratories in France (under experimentation), especially in large cities as Paris, Lyon, Toulouse, Lille, Marseille, Bordeaux, Rouen but also in transit places like theCharles de Gaulle airport and the Lyon-Macon TGV line.

5G and weather: can 5G frequencies in France have an influence on weather predictions as in the United States ?
A American study of the scientific journal Nature on 5G has highlighted the effects that might have the 5G frequencies on weather predictions in the United States. The frequencies envisaged for the development of 5G on the other side of the Atlantic will be located at first between 24.25 and 25.25 GHz.

THE Institutes dedicated to weather use data recorded by satellites To predict time. Water vapor, specifies the review, emits a signal of 23.8 GHz so very close to the frequency band that the United States wants to use, which could blur the signals of water vapor. (Sources Nature and the Parisian))
In Europe, thanks to precautionary principle, a guard band has been set up. So the bands between 24 and 25 GHz cannot be used. In France, the 25.5 – 26.5 GHz frequency band is operated by the Ministry of the Armed Forces, the National Center for Spatial Studies and the Météo Administration. In addition, as seen above, only frequencies 26.5-27.5 GHz are free for the moment for the use of 5G in 2020.
What is the precautionary principle ? Present in theArticle 191 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, THE precautionary principle aims to guarantee a level of Environmental Protection (including man) and prevention measures. Thus in the absence of sufficient scientific data, it is possible to prevent a decision as in this case the allocation of certain frequencies at risk, otherwise, the decision may be applied or not. (Eur-lex sources)
THE possible non-compliance with this limit for 5G frequencies by Americans would not only have consequences for forecasts on their own territory but also worldwide because all satellites are potentially concerned. The European Union is currently negotiating in an attempt to make them change their minds.
5G frequencies: What do we know about the effects of 5G on the health of future users ?
The arrival of 5G and reflection on these new frequencies once again raise a question that concerns more than one: can 5G have harmful consequences on the health of its future users ? THE Current 5G studies It is only for the beginnings and it is impossible to know more for the moment, however some scientists highlight the potential risks of this new network. For Annie Sasco, director of unit at International Center for Cancer Research, There is no doubt about it (words expressed on France Bleu Radio):
When you change the frequency, you modify the wavelengths and you can expect with 5G and the increase in frequencies which is very important, at risks which will be of the same nature, but probably more marked.
THE Research carried out on 2G, 3G and 4G networks show risks of development of brain and heart -hearted tumors But there are no links established with man.
There are approximately 200,000 relay-mobile antennas in France (According to the FFT) and there are chances only with the 5g There are many new arrivals. A Recommendation of the 1999 European Council of State established limits for exposure to electromagnetic waves (between 28 V/m and 87 V/m). It remains to be seen whether these will not be rejected for the5G installation. To find out more, you can consult our article Mobile Relais antennas: Linky of Telecoms ?.
5G
5G is an evolving mobile technology that supports new features. It is designed to deal with the exponential demand for connectivity and support new applications thanks to very large data flows (several gigabits), great reactivity (a low latency of the order of a few milliseconds) and great reliability.
Technical characteristics
The first deployments of 5G are carried out mainly in the 3.5 GHz frequency band which is a band very close to the current mobile networks (3G/4G and Wi-Fi) in terms of coverage. This means that many existing antennas sites can be reused for 5G, without adding new sites.
The main difference with existing networks will be lied in the use of intelligent MIMO antennas (in French: multiple outputs outputs), each of which is a large number of miniaturized antennas and which make it possible to reach flows and a capacity transmission inaccessible today in 4G.
These intelligent antennas emit radio waves where the need for connection claims it. Being directional, they emit only on demand, that is to say only at times when terminals need to connect to the network. And unlike conventional antennas which emit without discontinuity on the whole of a geographic area (cells), they serve on demand the terminal which declares itself on the network.
This characteristic allows antennas to stand in standby when they are not activated, hence better management of energy consumption.
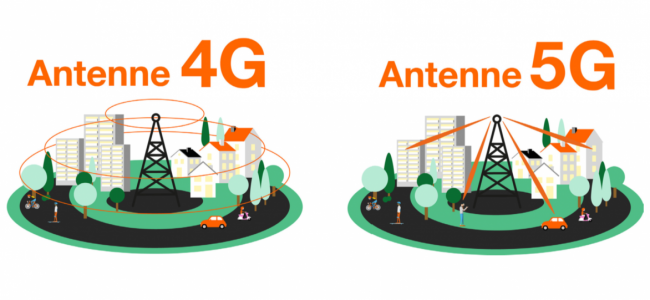
In addition, in certain network cells, small additional antennas can be installed in order to provide additional coverage and capacity to certain “blind” areas. These small complementary antennas can be located on urban furniture or inside buildings.
Secondly, to achieve larger speeds (close to those of fiber), 5G will use higher frequencies at 26 GHz. This frequency band, called “millimeter waves”, is already used by certain services such as speed radars, vehicle anti-collision systems, airport safety gantries ..
The regulatory and sanitary framework
5G follows the international directives of the ICNIRP (International Commission for the Protection of Non -Ionizing Radiations) and the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) recognized by the World Health Organization.
The frequencies used by 5G are part of the radio waves in which thousands of studies have been devoted for more than 20 years. After systematic analysis of all these studies, the national and international health authorities have concluded that the health is noted for health below the thresholds defined by international directives.
These thresholds are included in European regulations n ° 1999/519/EC of 07/12/99 and their validity was very recently reconfirmed by the Commission in a parliamentary response in May 2019.
One note, however: with the arrival of 5G, it could be found to be slight increases in global exposure to radio waves when added to an existing network. However, this exposure will remain very low with regard to / much lower than the authorized limits. International CEI standards (International Electrotechnical Commission) and CENELEC (European Electronic and Electrotechnical Standcase Committee) already allow you to assess the exposure levels and compliance of antennas and 5G mobile phones.
As a reminder: the exposure limit of the 5G antennas to 3.5 GHz and beyond is 61v/m and the 5G mobile phones (operating at 3.5 GHz) must not exceed 2W/kg (for DAS ) just like the existing terminals in 2G, 3G and 4G.



